Description
Dion – Torch Relay Greek Route
Athens 2004 Olympic Games Pin
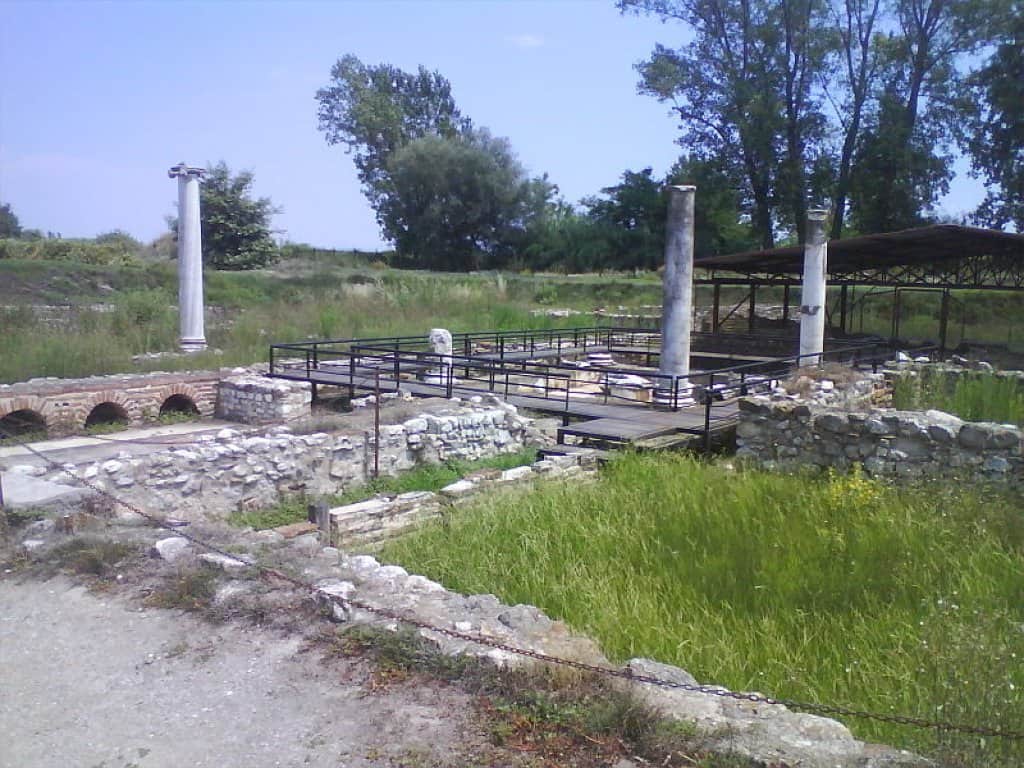
The Olympic Flame past from Greek City, Dion.
The 2004 Summer Olympics Torch Relay took the Olympic Flame across every habitable continent, returning to Athens, Greece. Every citywhich had hosted the Summer Olympics was revisited by the torch, as well as several other cities chosen for their international importance.
The relay was the first time the Olympic flame had travelled to Africa, India and South America. The flame was transported from country to country aboard a specially-equipped Boeing 747 leased from Atlanta Icelandic (Registration TF-ARO) called Zeus. On board the flame was carried and burned continuously in specially modified miners lamps.
Dion or Dio is a village located at the foot of Mount Olympus and in the municipality of Dio-Olympos.
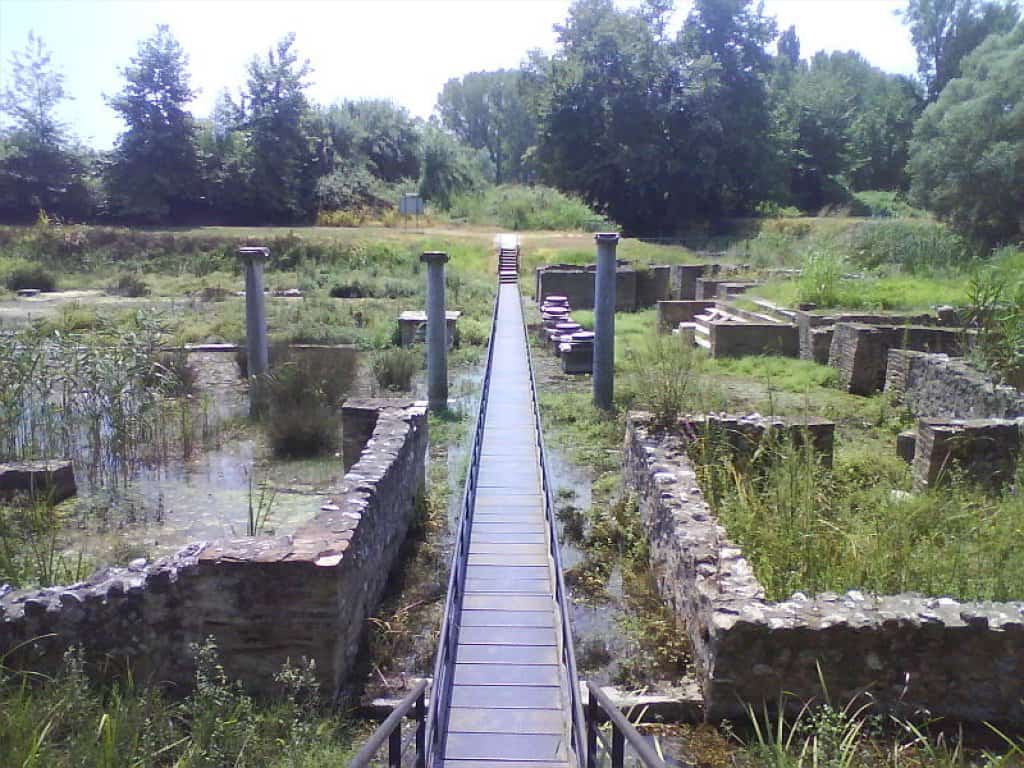
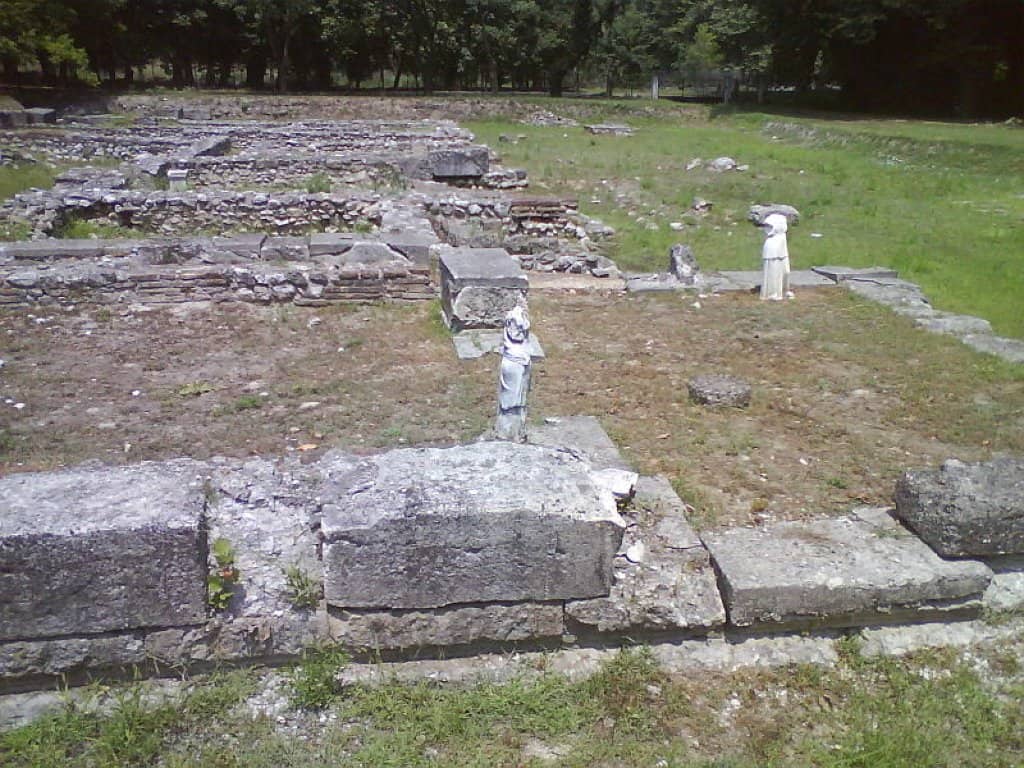
It is best known for its ancient Macedonian sanctuary of Zeus and city, visible in the archaeological park and the Archaeological Museum of Dion.
The site of ancient Dion was first identified by the English traveler William Martin Leake on December 2, 1806, in the ruins adjoining the village of Malathria. He published his discovery in the third volume of his Travels in Northern Greece in 1835. Leon Heuzey visited the site during his famous Macedonian archaeological mission of 1855 and again in 1861. Later, the epigraphist G. Oikonomos published the first series of inscriptions. Nevertheless, systematic archaeological exploration did not begin until 1928. From then until 1931, G. Sotiriadis carried out a series of surveys, uncovering a 4th-century BC Macedonian tomb and an early Christian basilica. Excavations were not resumed until 1960 under the direction of G. Bakalakis in the area of the theatre and the wall. Since 1973, Professor D. Pandermalis of the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki has conducted archaeological research in the city.
Dion is the site of a large temple dedicated to Zeus, as well as a series of temples to Demeter and to Isis (the Egyptian goddess was a favorite of Alexander).
Excavation of the magnificent House of Dionysos revealed a mosaic of exceptionally fine quality.
A rare and unusual find in the museum is a bronze “hydraulis” or hydraulic musical pipe organ found in a former workshop.
In 2006, a statue of Hera was found built into the walls of the city. The statue, 2200 years old, had been used by the early Christians of Dion as filling for the city’s defensive wall.
The pin depicts the Torchbearer passing from a monument of Dion city
Product: Olympic Pin
Pin code: #04-162-088
Tiraz: <1.000pcs
Official Licensed Product
Licensed Manufacturer: Efsimon Collection







Reviews
There are no reviews yet.